Welding titanium and titanium alloys demands precision and expertise to ensure flawless results. Here, we delve into the meticulous process required to master this specialized form of welding.
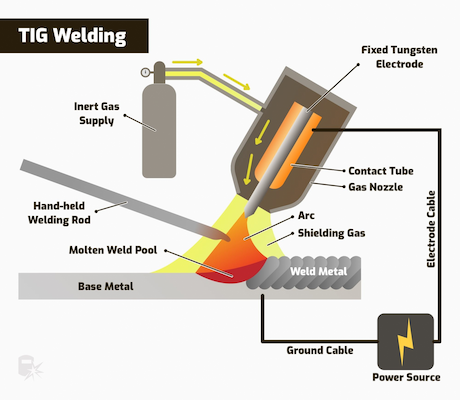
Choosing the right welding method is crucial when working with titanium and its alloys. For thin sheets below 3 millimeters, tungsten inert gas (TIG) welding is recommended for its delicate control, ensuring seamless welds. For thicker sheets exceeding 3 millimeters, plasma arc welding stands out for its efficient melting capabilities. Advanced techniques like submerged arc welding and vacuum electron beam welding are also viable options, tailored to specific project requirements.
Detailed Pre-Weld Preparations
- Surface Cleaning:
Mechanical cleaning involves using fine sandpaper, stainless steel wire brushes, or hard alloy scrapers to eliminate oxidation and impurities from the welding area.
Chemical cleaning employs specific acid solutions like a mixture of HF and HNO3 for deep cleansing, followed by rinsing with clean water and drying to ensure a residue-free surface.
- Equipment and Materials:
Opt for a direct current TIG welding power source with high-frequency arc initiation and stable characteristics to maintain welding process stability.
Ensure the purity of argon gas is above 99.99% and continuously supplied until the weld cools completely to prevent oxidation.
Match the welding wire with the base material composition or opt for a slightly lower-strength wire to enhance weld ductility as per requirements.
- Precise Welding Procedures:
Gas Shielding
Employ dedicated shielding hoods to protect the weld zone and weld seam from harmful gases while maintaining temperatures below 250°C.
Skillful Operations
Maintain a small angle between the welding wire and workpiece, smoothly feeding it into the molten pool to avoid excessive lateral movement, ensuring uniformity and quality of the weld seam.
Continuous Protection
When ending the arc and finishing the weld seam, continue argon gas shielding until the weld and the heat-affected zone cool down to a safe temperature.
Stringent Weld Seam Inspection
By observing the color of the weld seam, preliminary assessments of the weld quality can be made. An ideal weld seam exhibits a silver-white or light yellow color, while deeper yellow and golden-purple shades vary in acceptance based on weld seam grades. A deep blue color indicates substandard welding quality.
Vital Considerations Not to Overlook
Maintain strict control over welding parameters to ensure process stability and weld quality.
Uphold cleanliness in the welding environment to prevent contaminants from entering the welding zone.
Welding personnel should undergo professional training to proficiently grasp the welding characteristics and operational norms of titanium and titanium alloys.




